| 2766-6863 | |
| 2766-6863 (service hours) | |
| Online Form | |
| Contact your Faculty Librarians on in-depth research questions |
Literature review is an indispensable step in academic research. To accelerate this process, AI OneSearch Lite and Scite are two of the available GenAI tools for PolyU students:
Users are required to login to access AI OneSearch Lite.
Learn more about the details of the above key features and how AI OneSearch Lite complements OneSearch!
The Library's subscription to Scite is available to all PolyU staff and students. To access premium features, please sign up for a scite account or log in to your existing one.
Getting Started with Scite Assistant
The default tab on the homepage is Scite Assistant. It answers questions in natural language based on scholarly sources and allows you to refine its search with customizable settings. There are also 3 additional options to customize your responses:
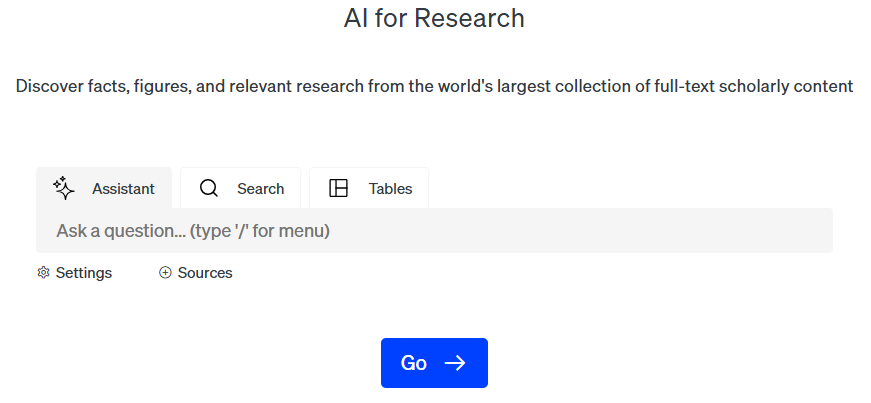
⚠️Importance of critical thinking when using Scite Assistant⚠️
Scite Assistant's responses are not guaranteed to be 100% accurate. Never copy Scite Assistant's responses and submit as your own work. You are accountable for your work and should use these responses responsibly.
| Strengths | Weakness |
|---|---|
|
Efficiency Quickly synthesizes information from a vast amount of search results Example: |
Incomplete Information
(Tip: Check whether the important journals in your field are indexed and what is covered in Scite before using) |
|
Complex Queries
Example: What are the unexplored areas in the study of student procrastination? |
Citation Accuracy Although citations are included, they do not always accurately support the claims made. Here is an example of a misleading indirect citation.
|
|
Personalized UX Tailors information to your specific needs Example: What are the most effective strategies for undergraduates to combat procrastination? Provide a summary of the top 5 approaches and rank according to their effectiveness. |


Customize your Experience
To optimize the outputs of Scite Assistant, read Scite's free e-book, AI Prompt Handbook For Scite Assistant: Optimize AI Outputs & Accelerate Your Research, to understand how it works and compare prompts used at Scite Assistant.
Additionally, Scite Assistant also offers features to enhance your experience. Find out how:
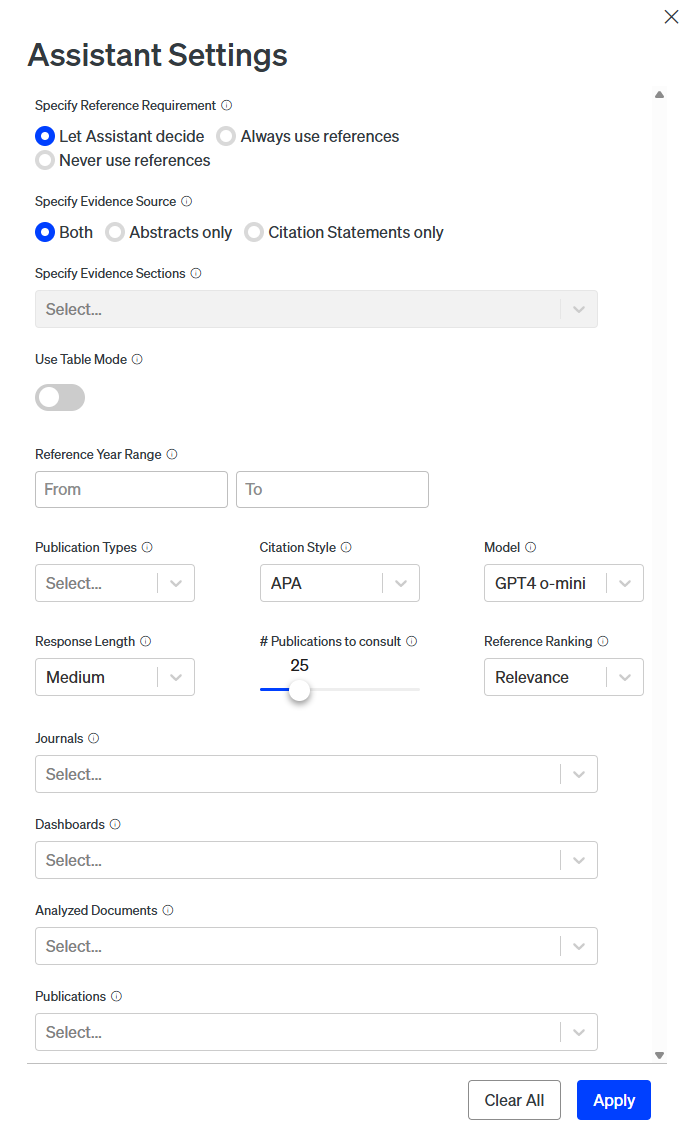
Scite Assistant offers customizable settings via the  button to refine prompt processing. Key options include:
button to refine prompt processing. Key options include:
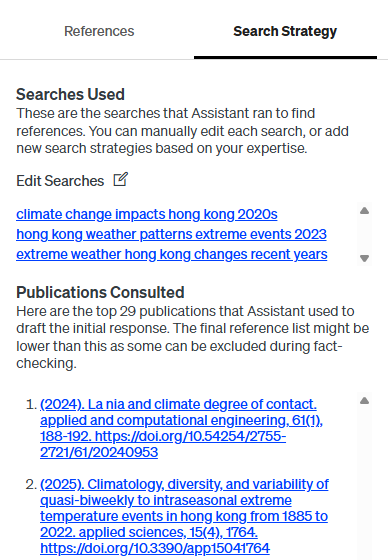
Customize your search in Scite Assistant via the “Search Strategy” tab. Click “Edit Searches” to review, add, or remove keywords, tailoring the tool to your research needs.
What are citation statements?
A citation statement refers to the sentence(s) surrounding a citation within a publication. It provides context for the citation with the search term and illustrates how other authors are citing another source.
Why do I need to search for citation statements? How can they help with my research?
Citation statement search not only helps you retrieve relevant works, but also directly shows the relevant citation statements within those works. This can help speed up:
For each publication on the search result list, there are indices that categorize citation statements into three types: (1)  supporting, (2)
supporting, (2)  mentioning, and (3)
mentioning, and (3)  contrasting, to help researchers quickly grasp how the work has been cited by the others and hence the impact of the work. The
contrasting, to help researchers quickly grasp how the work has been cited by the others and hence the impact of the work. The  number of publications citing the work is also shown.
number of publications citing the work is also shown.
For example, for the following work, there are 2,219 publications citing this work,

From the search result list, each of the retrieved citation statements is also categorized, with a confidence percentage reflecting how certain Scite is about its classification.

Further Reading: How are citations classified?
After clicking into a publication from the search results, you will arrive its report page.
The report page helps researchers to quickly evaluate a publication and understand its impact. It shows a paper's citation count, and how it is cited by others, including the citation statement and smart citations.

Further Reading: How do I use the scite report page?
Here are some popular AI-powered research tools that can also assist you in literature discovery. Please note that these tools are currently not subscribed to by the library, so access may vary.
Semantic Scholar offers search functions similar to search engines and academic databases, but with enhanced AI capabilities, including:
📌 Tip: Semantic Scholar may provide a publisher's link to the academic paper in the search results. To read the full-text of these sources, install library browser plug-ins to access them directly from publisher's webpage, bypassing the library webpage.
How do librarians view different AI-powered research tools? Check out the information and in-depth discussions at the following links.
By Aaron Tay, Singapore Management University Libraries
By Aster Zhao, HKUST Library
By Birmingham City University Library & Learning Resources